SIMCom LTE Cat.1 Modules Are Causing a Sensation in the Market
Mr. Wen Ku, who serves as the spokesperson for the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and leads the Information and Communications Development Division, announced on October 22, 2019, that China presently possesses 1.257 billion 4G subscribers, constituting 78.8% of the total mobile phone user base.
The widespread adoption of 4G has reached a significant level, prompting the need for 2G and 3G technologies to phase out from the market. Telecom carriers are actively encouraged to guide users in transitioning to newer networks, thereby utilizing limited frequency and network resources for the advancement of 5G and 4G mobile communication networks. This approach aims to reduce overall costs and enhance the operational efficiency of national communication networks.
Consequently, with the eventual retirement of 2G and 3G networks, the predominant role will be assumed by 4G and 5G networks. A prevailing viewpoint suggests that the middle ground, encompassing medium-rate technologies (such as Cat.1 and eMTC (cat.m)), will bridge the gap between high-rate (5G and 4G LTE) and low-rate (2G GPRS and NB-IoT) connections. This anticipates a surge in the adoption of LTE Cat.1 technology.
In accordance with recent research by Counterpoint Research, the year 2020 is projected to witness the connection of 50 billion devices to the Internet, with a market size reaching $19 trillion. Such extensive data accessibility is poised to catalyze a transformation within the IoT market.
Nevertheless, the current landscape indicates that only 10% of scenarios, such as telemedicine and autopilot systems, demand high-rate connectivity. In contrast, 60% of scenarios, including metering and city management applications, require transmitting only a small number of bytes per day, making them ideal candidates for low-rate NB-IoT connections. Consequently, the remaining 30% of the market will be dominated by LTE CAT-1 and eMTC connections. According to a recent research report by the Global Mobile Suppliers Association (GSA), 102 carriers across 52 countries have implemented or introduced Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) primarily driven by NB-IoT and LTE-M technologies. Among these, 20 carriers concurrently employ both standards, while more than 140 carriers continue to invest in NB-IoT and LTE-M to support upcoming IoT devices and applications.
NB-IoT technology can address the technical void left by the discontinuation of 2G networks, serving the demand for affordable low-rate transmissions. LTE-M offers greater bandwidth and can achieve transmission rates of up to 1Mbps, significantly surpassing the maximum upload/download rates of NB-IoT. This allows for increased data throughput. Consequently, Cat.1 and eMTC can cater to markets requiring voice and medium- to low-rate data transmissions. However, when compared to Cat.1, eMTC’s prospects in China are limited, making Cat.1 the favored choice for 30% of the medium-rate cellular communication module market.
SIMCom has long been strategizing the implementation of LTE Cat.1 technology. In 2015, SIMCom introduced the LTE Cat.1 module SIM7500CE, amassing extensive expertise in Cat.1 products and services across various fields, including positioning and tracking, low-speed gateways, intelligent monitoring, and secure payment systems. In response to the burgeoning demand for LTE Cat.1 technology, SIMCom has launched a series of LTE Cat.1 modules.
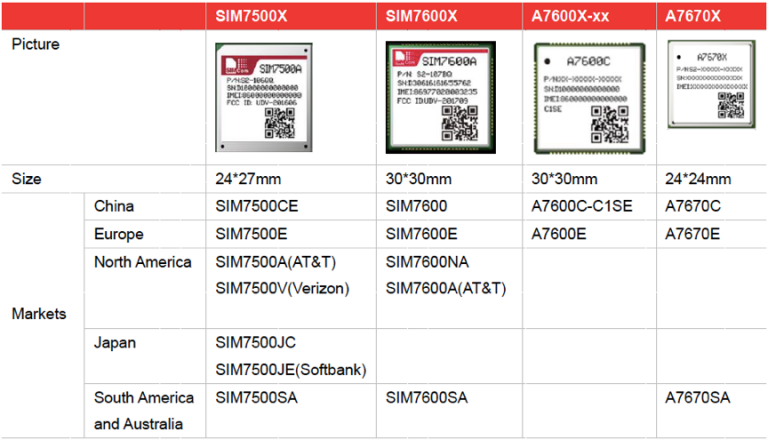
Variants of SIMCom Cat 1
SIMCom Cat 1 technology is categorized into the following versions:
A7670X – Ultra-compact 4G module, compatible with 2G/3G/NB networks (New Arrival)
A7600x-xx – Cost-effective Cat1 module catering to diverse market segments, offering cost-saving benefits (New Arrival)
SIM7600G module LTE Cat1 global version all-in-one (New Arrival)
SIM7600X – Highly reliable module for industrial applications
SIMCom’s LTE Cat.1 modules facilitate rapid upgrades from 2G/3G/4G networks while accommodating various cost requirements in different application market segments. When compared to NB-IOT and LTE Cat.4 technologies, they offer a range of cost advantages.
1. Network Infrastructure
Global deployment of 4G LTE networks follows the streamlined 3GPP Release 8 protocol, enabling seamless integration of SIMCom LTE Cat.1 modules into existing LTE networks, thus resulting in cost-effective network coverage.
2. Chip Costs
Following system optimization, higher integration and simplified hardware architecture of modules contribute to lower peripheral hardware costs.
3. Latency
SIMCom LTE Cat.1 modules exhibit comparable millisecond latency to LTE Cat.4 modules. They are also capable of supporting movement speeds exceeding 100KM/H, all while offering a nearly 30% lower cost than Cat 4 modules.

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt  English
English